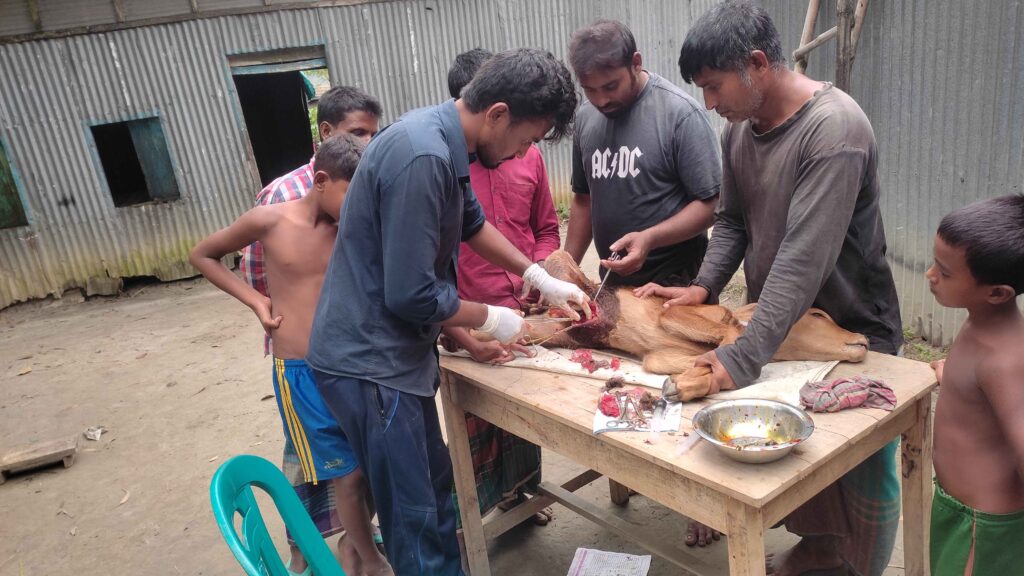
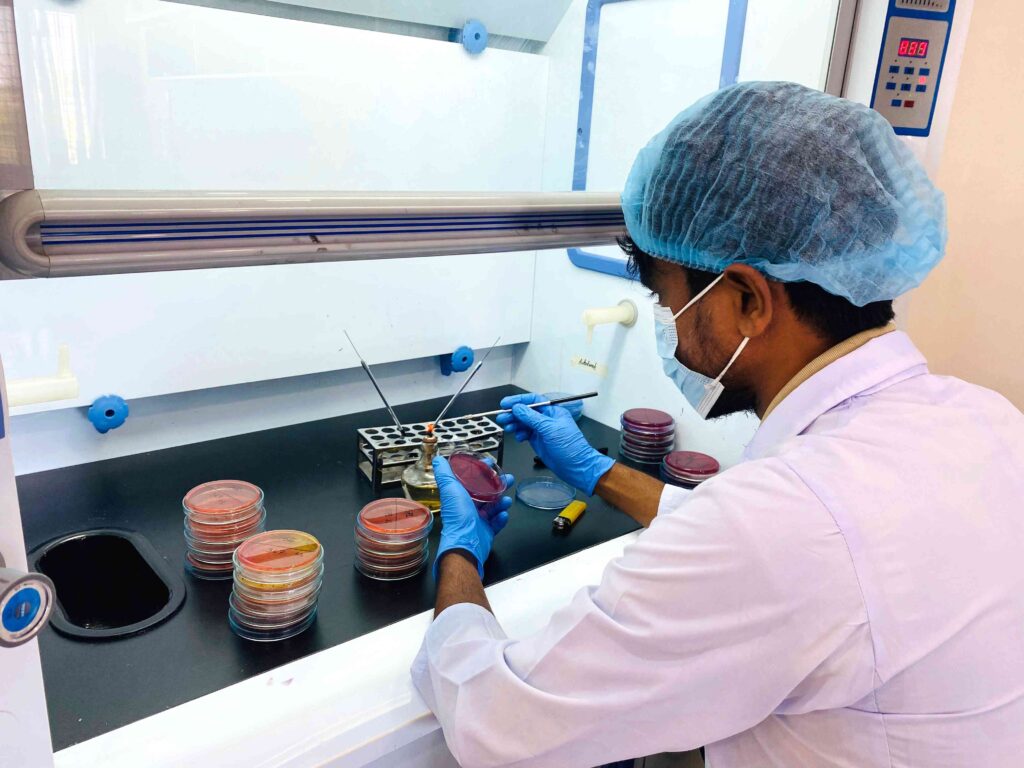
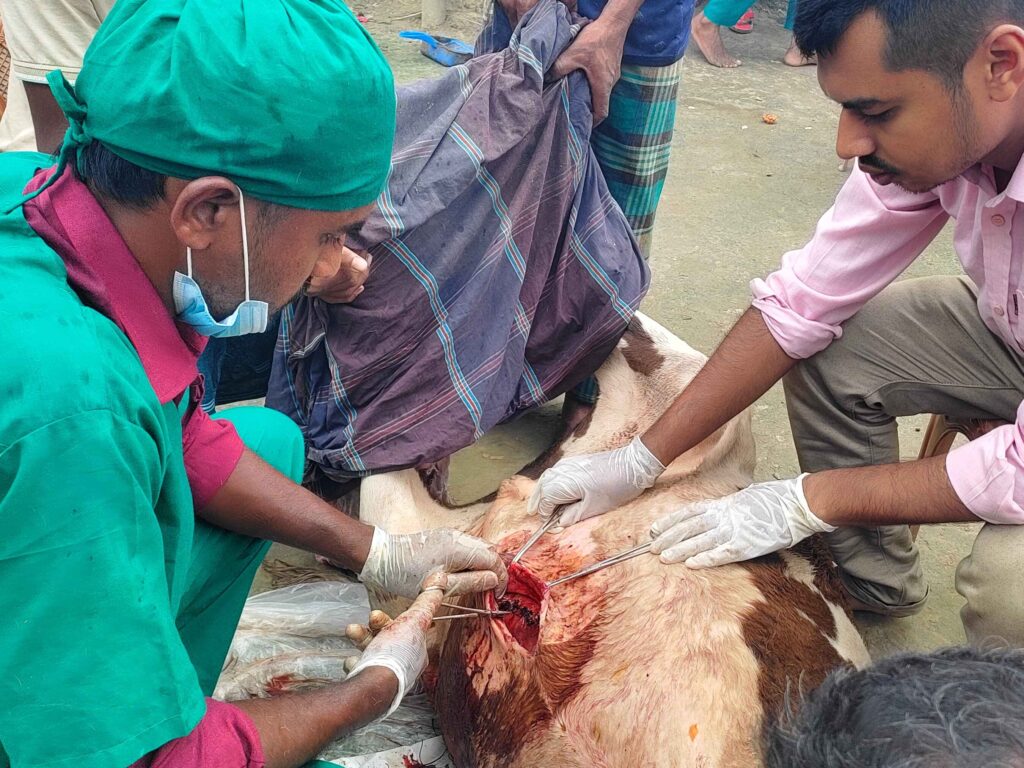
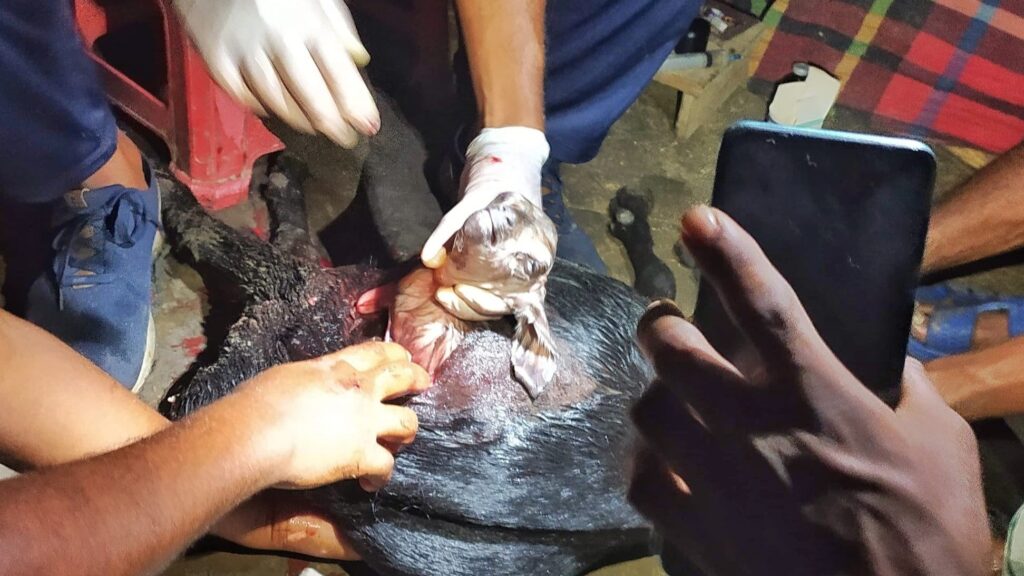
Veterinary Science: Importance, Scope, and Career Opportunities Introduction Veterinary Science is a vital branch of medical and biological sciences that focuses on the health, welfare, and management of animals. It plays a crucial role not only in treating animal diseases but also in safeguarding public health, ensuring food safety, and supporting sustainable agricultural development. In countries where agriculture and livestock are key economic sectors, veterinary services are indispensable. What is Veterinary Science? Veterinary Science deals with the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of diseases in animals, including livestock, poultry, companion animals, and wildlife. Veterinarians are trained to manage animal health, improve productivity, and prevent zoonotic diseases—illnesses that can be transmitted from animals to humans, such as Rabies, Anthrax, and Avian Influenza. Importance of Veterinary Science 1. Animal Health and Welfare Veterinary professionals ensure proper diagnosis, treatment, and preventive care for animals. Healthy animals experience less suffering, live longer, and perform better in terms of productivity. 2. Food Safety and Quality Milk, meat, eggs, and other animal-based products are essential sources of nutrition. Veterinary inspection and disease control ensure these foods are safe for human consumption and free from harmful pathogens. 3. Public Health Protection Many human diseases originate from animals. Veterinary Science plays a key role in monitoring, preventing, and controlling zoonotic diseases, thereby protecting communities and reducing public health risks. 4. Economic Development Livestock and poultry sectors contribute significantly to national economies. Effective veterinary services reduce animal mortality, increase production efficiency, and improve farmers’ income. Roles and Responsibilities of Veterinarians Scope of Veterinary Science The scope of Veterinary Science is broad and continuously expanding. Graduates can work in: Career Opportunities in Veterinary Science Veterinary graduates can pursue diverse and rewarding careers, including: Veterinary Science offers long-term career stability, social respect, and global demand. Future Prospects of Veterinary Science With increasing concerns about food security, emerging diseases, climate change, and sustainable farming, the demand for skilled veterinary professionals is growing rapidly. Advanced technologies such as precision farming, disease surveillance systems, and biotechnology are further expanding the scope of this field. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) Q1: Why is Veterinary Science important? Veterinary Science is essential for maintaining animal health, ensuring food safety, preventing zoonotic diseases, and supporting economic development. Q2: What are zoonotic diseases? Zoonotic diseases are infections that can spread from animals to humans, such as Rabies, Bird Flu, and Anthrax. Q3: Is Veterinary Science a good career choice? Yes, it offers diverse career opportunities, job security, social impact, and increasing global demand. Q4: Who can study Veterinary Science? Students with a background in science, particularly biology, can pursue Veterinary Science through recognized academic programs. Q5: How does Veterinary Science contribute to agriculture? It improves livestock productivity, reduces disease-related losses, and supports sustainable farming practices. Conclusion Veterinary Science is a multidisciplinary field that bridges animal health, human well-being, and environmental sustainability. Investing in veterinary education and services is essential for building a healthier society, ensuring safe food systems, and promoting sustainable economic growth.